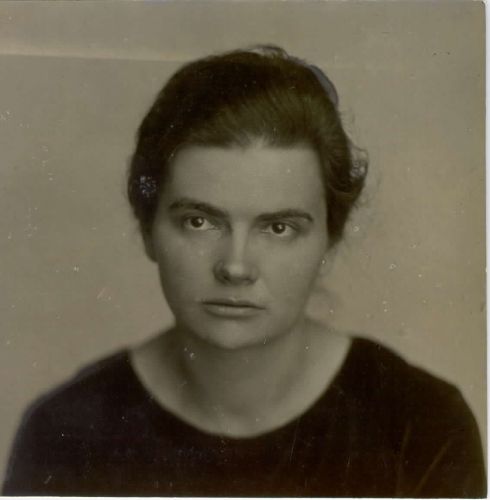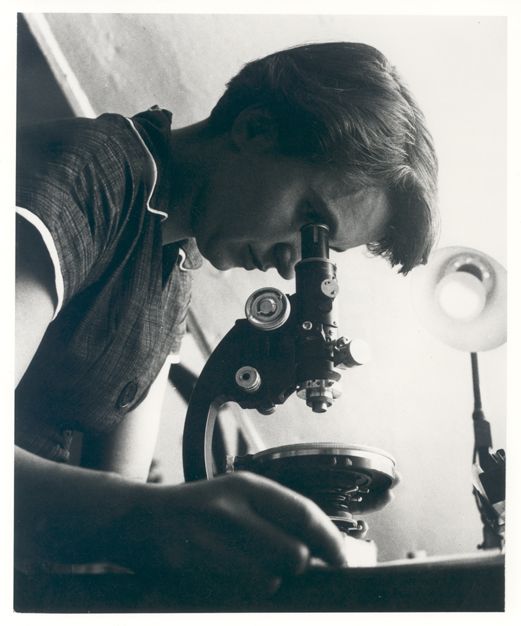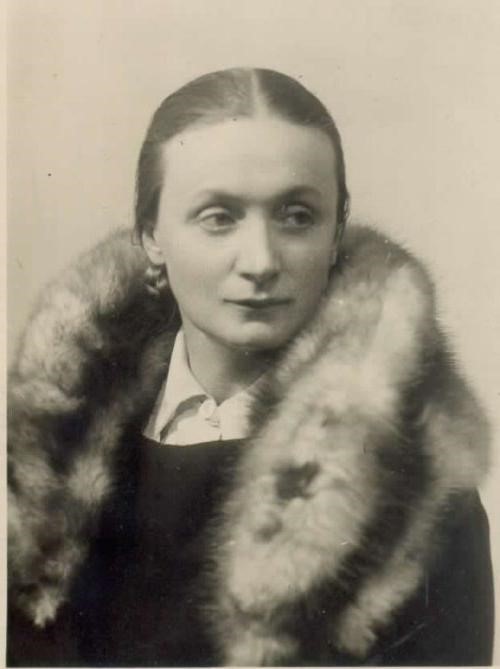
Elvira Kralj  1900 – 1978
1900 – 1978
Too nice to be remembered?
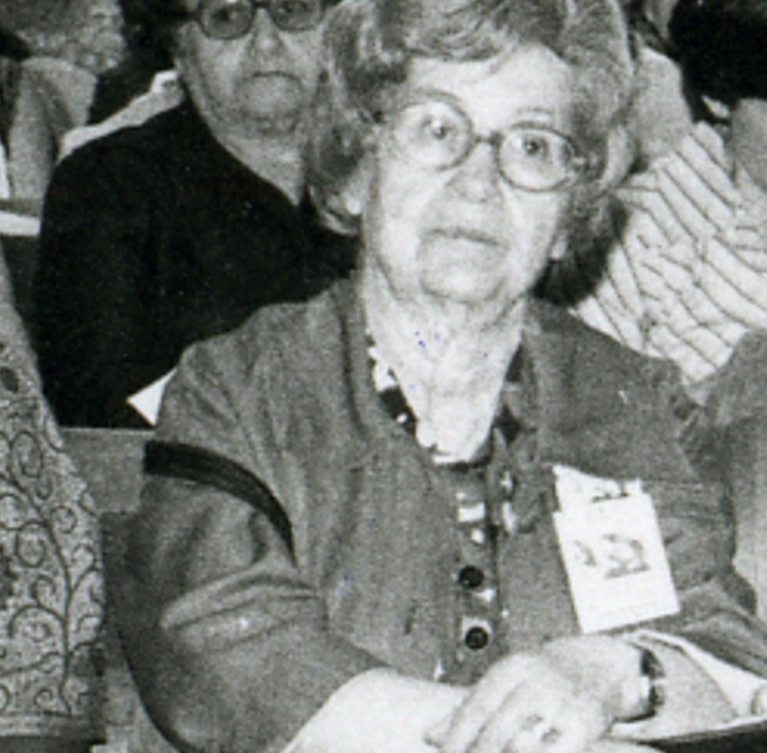
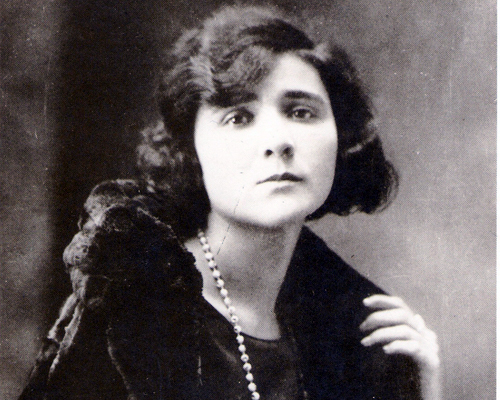
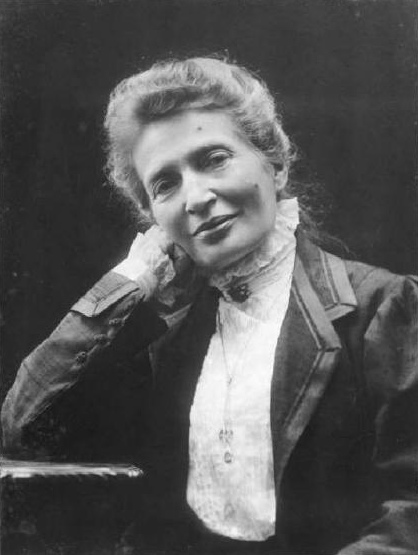
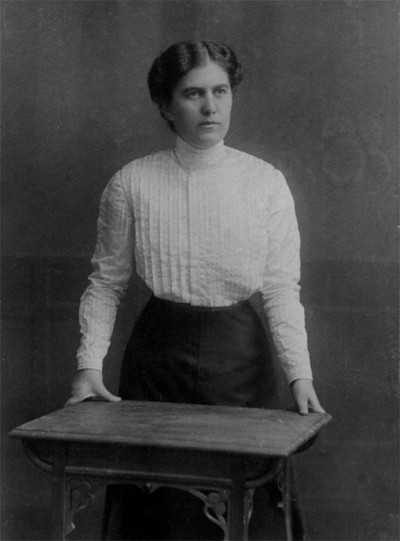
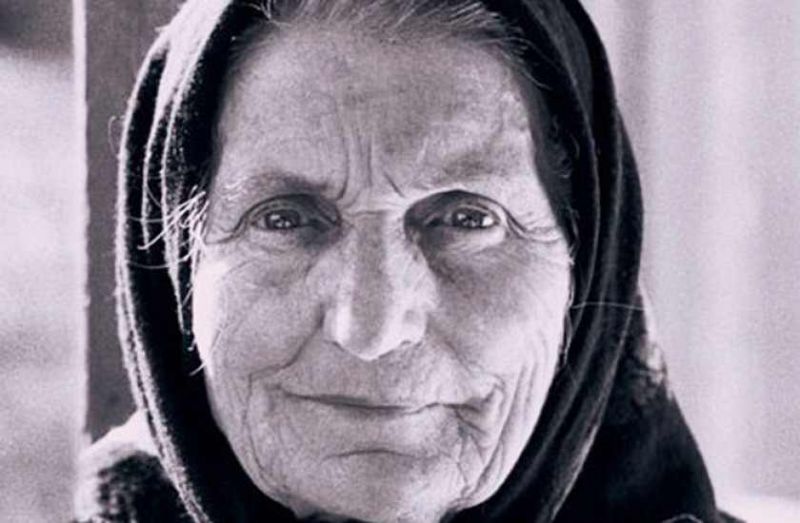
Elvira Kralj was a Slovenian actress born in Trieste (then part of Austro-Hungarian Empire). She was born into a family that was politically engaged in defending the Slovenian national cause. The whole family was related to Sokol, a left-wing association addressing physical culture. Elvira was a member of several associations embracing different social causes though not the women’s cause specifically.
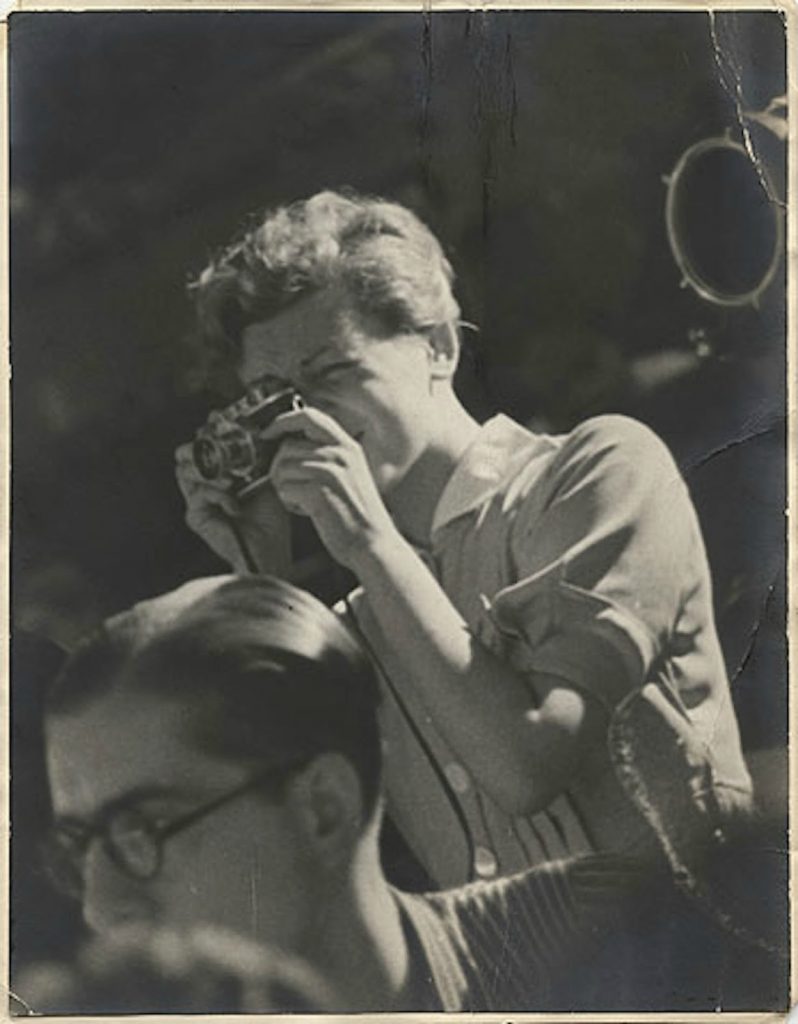
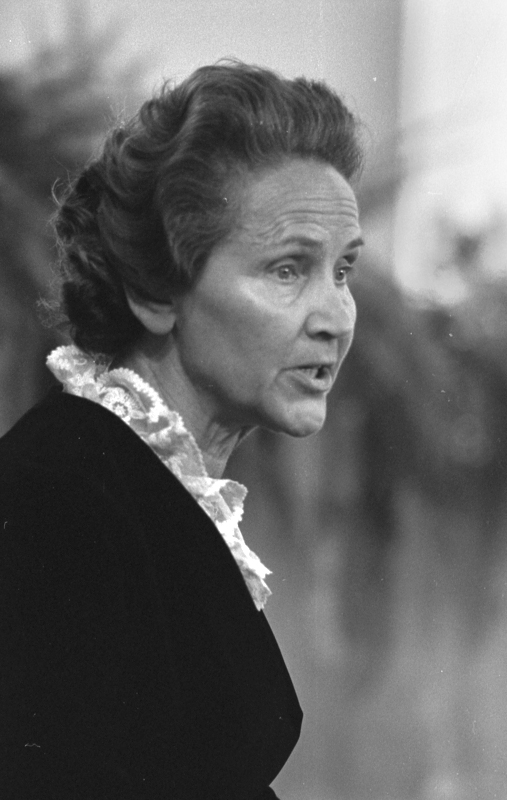
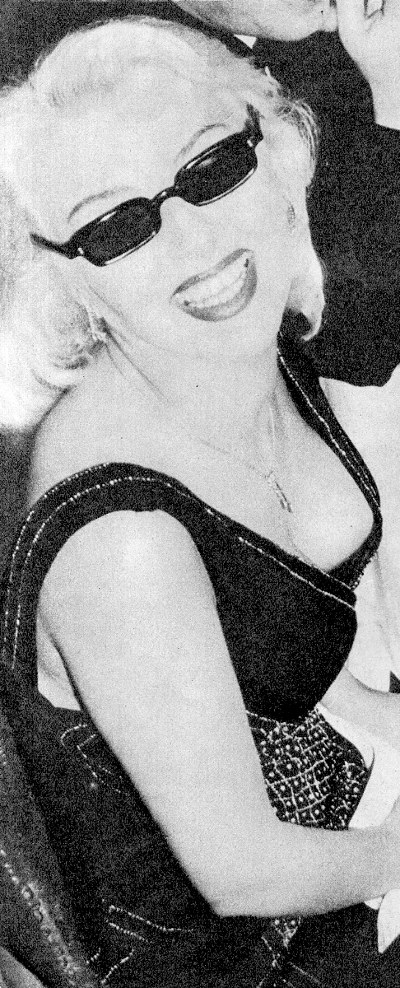
She started acting at the age of five when she played Cinderella on a stage in Trieste. After completing her studies in the local German Elementary School and two years of studies at the German Higher Trade School for Girls – boys and girls attended different schools, she started working in a law firm in Trieste. Later she graduated from a Drama school. She embodied more than 200 roles in the Maribor Theatre, and began working in the Ljubljana’s Drama, the national theatre. She convincingly portrayed a multitude of different female characters, from a kind grandmother, a nice aunt, a suffering mother, a tough woman, to evil, ironic characters on the theatre stage, TV and film screen. Her most visible role was that of the kind, loving and caring aunt (typically accepted female characteristics) in the iconic film Do Not Wait for May. Why was Elvira belittled? Despite her many roles for which she was casted...
continue reading
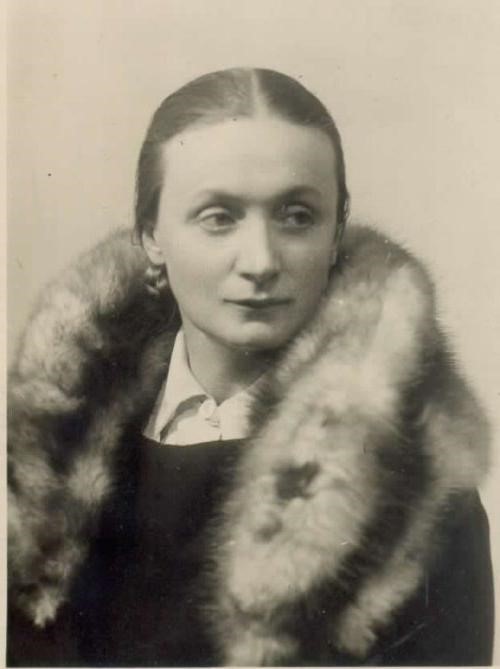
Elvira Kralj  1900 – 1978
1900 – 1978
Too nice to be remembered?
Elvira Kralj was a Slovenian actress born in Trieste (then part of Austro-Hungarian Empire). She was born into a family that was politically engaged in defending the Slovenian national cause. The whole family was related to Sokol, a left-wing association addressing physical culture. Elvira was a member of several associations embracing different social causes though not the women’s cause specifically.
She started acting at the age of five when she played Cinderella on a stage in Trieste. After completing her studies in the local German Elementary School and two years of studies at the German Higher Trade School for Girls – boys and girls attended different schools, she started working in a law firm in Trieste. Later she graduated from a Drama...
continue reading
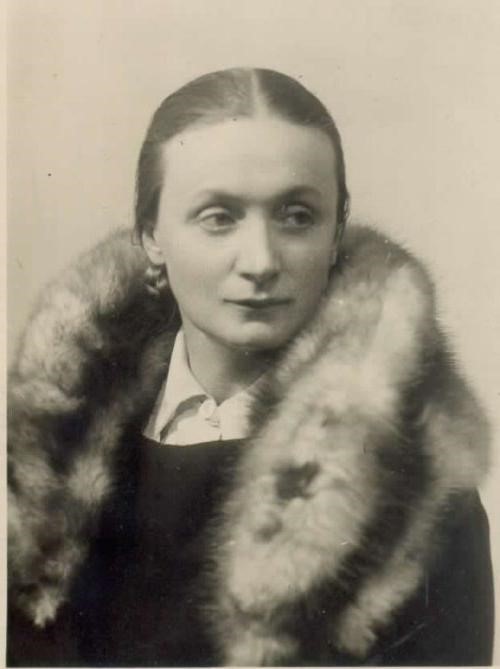
Elvira Kralj  1900 – 1978
1900 – 1978
Too nice to be remembered?
Elvira Kralj was a Slovenian actress born in Trieste (then part of Austro-Hungarian Empire). She was born into a family that was politically engaged in defending the Slovenian national cause. The whole family was related to Sokol, a left-wing association addressing physical culture. Elvira was a member of several...
continue reading